Sign up. Be inspired. Get clicking.
SAF environmental benefits: Is the future of aviation sustainable?
1 January 2023
We are on the brink of a new era in aviation. This era is marked by the rise of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF). It's an alternative energy source that could significantly reduce the industry's carbon footprint.
SAF is a safe and almost identical replacement for traditional jet fuel. It can cut emissions by up to 80% across its lifecycle. This could lead to even larger reductions in the future.
We at CarbonClick Supply Sustainable Aviation Fuel, to enquire of our service please click here
This innovative solution is key to helping the aviation sector reach net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. It's a substantial step towards a more sustainable future for air travel.
The benefits of SAF for the environment are clear. U.S. transportation emissions from aviation are between 9% and 12%. Using this renewable fuel can significantly reduce these emissions and help fight climate change.
There are many feedstock options for SAF, including biomass and waste. This makes it a promising choice for a more sustainable and varied energy landscape in aviation.

What is Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)?
Defining SAF and its potential impact
Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) is a biofuel for planes. It's like regular jet fuel but better for the environment. It can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, sometimes even resulting in negative emissions.
SAF is crucial for lowering aircraft emissions, which contribute significantly to U.S. transportation pollution. Using SAF can help decrease these emissions.
SAF can be blended with conventional jet fuel, allowing planes to use it without requiring modifications. However, currently, only a small proportion of jet fuel is SAF. Nevertheless, increased investment is being directed towards making SAF more accessible and affordable.
The goal is for planes to be carbon neutral by 2050. Sustainable aviation fuel can cut CO2 emissions by up to 80%. This makes SAF a substantial benefit for the environment. It also leads to reduced pollution from sulphur and particulates.

SAF's Role in reducing carbon emissions
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is key for the aviation industry to cut carbon emissions. Using 100% SAF can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 94%. This is crucial for the sector's aim to reach net-zero carbon by 2050, promoting aviation decarbonisation and sustainable air travel.
SAF also reduces harmful emissions like particulates by 90% and sulphur by 100%. It can lower lifecycle carbon emissions by up to 80%. This is vital for reducing the aviation industry's impact on the environment and moving towards sustainable fuels.
Even though SAF has many benefits, it currently makes up only 0.1% of jet fuel used. We need to accelerate SAF production and usage to truly lessen the aviation industry's carbon footprint. As more people seek sustainable air travel, SAF's role in emissions reduction and aviation decarbonisation will become increasingly significant.
A menu of sustainable feedstocks for producing SAF
The aviation industry is working hard to reduce its environmental impact. Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is a key player in this effort. It's made from renewable biomass sources, offering many options for sustainable air travel.
Exploring Various Renewable Feedstock Options
In the United States, about 1 billion dry tons of biomass can be collected each year. This amount can produce 50–60 billion gallons of biofuels. The SAF feedstocks include corn, oil seeds, algae, fats, oils, and greases, as well as agricultural and forestry residues.
These renewable biomass sources are sufficient to fuel the U.S. aviation industry. They also provide fuel for other transport modes and valuable bioproducts.
The world of sustainable aviation fuel production is expanding. New methods and technologies are being developed to utilise biofuel raw materials more effectively. By converting waste into fuel, the aviation sector can lower its carbon emissions and move towards a more sustainable future.


Benefits of SAF beyond lowering GHG emissions
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) does more than just reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It also fosters economic growth in farming areas, aids the environment, and enhances aircraft performance.
Environmental Services and Improved Aircraft Performance
SAF is made from renewable and waste materials. This process benefits farms and the environment by preventing erosion, improving water quality, boosting biodiversity, and sequestering carbon in the soil.
SAF also originates from wet waste such as manure and sewage sludge. This reduces pollution and prevents methane from damaging the atmosphere.
SAF burns more cleanly in aircraft engines, leading to fewer harmful emissions near airports. It also decreases the formation of contrails, which adversely affect the climate. A 50% SAF blend can lower particulate emissions by up to 65% and oxides of sulphur by nearly 40%.
Using SAF makes planes more efficient and reduces emissions. This helps the aviation industry be more sustainable. It's a step towards a more responsible future for flying.
Biofuels production supports American jobs
The United States is making a significant push for Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF). This initiative is beneficial for creating jobs and boosting the economy in rural areas. As we work to reduce aviation's carbon emissions, increasing the production of biofuels opens up many job opportunities. These jobs range from growing feedstocks to building and operating biorefineries.
In farming communities, the demand for SAF feedstocks is revitalising the economy. It's creating jobs in growing, harvesting, and transporting these renewable resources. Additionally, constructing modern biorefineries to produce SAF is generating jobs in manufacturing and engineering. These positions are emerging in both urban and rural areas.
The use of SAF will also support the aviation industry. It will sustain jobs for pilots, crew members, and maintenance workers. Furthermore, it will create new jobs as the industry shifts towards cleaner, more efficient flying.
By investing in SAF production, the United States is reducing aviation's environmental impact. It's also securing the economic benefits of this expanding industry. Utilising renewable feedstocks, advanced biorefineries, and a skilled workforce is a crucial step towards a more sustainable and prosperous future for aviation in the nation.


BETO research brings more SAF to the market
To meet U.S. and aviation environmental goals, our researchers at the Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) are working diligently. They are developing new methods to produce sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). This includes utilising various renewable and waste materials to make SAF more accessible for planes.
Emerging SAF pathways and technologies
Our BETO-funded projects are investigating new approaches to produce SAF. This involves converting wet waste and bio-based materials into SAF that meets strict standards. We're also exploring whether carbon-rich waste gases can be used to create SAF.
We're collaborating with laboratories and industry partners to test and certify these new SAF methods. This ensures they are compatible with current aircraft and fuel systems.
The Biden administration has ambitious plans for SAF, aiming for 3 billion gallons by 2030 and 35 billion by 2050. Our research is crucial to achieving these targets. By exploring SAF research and development, novel production pathways, and waste-to-fuel conversion, we're helping make air travel more sustainable.
SAF environmental benefits: Reducing aviation's carbon footprint
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is key to cutting the aviation industry's carbon emissions. It aims to keep emissions at 2020 levels until 2035 and reach net zero by 2050. Using 100% SAF can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 94%, making it vital for decreasing the industry's carbon footprint.
SAF can lower CO2 emissions by 80% compared to regular jet fuel. In 2023, over 600 million litres of SAF were used, doubling the 2022 amount. Yet, this only accounts for 0.2% of all aviation fuel, highlighting the need to increase SAF production and support aviation decarbonisation.
The aviation sector is responsible for 2-3% of global GHG emissions, with 12% of transportation CO2 emissions originating from it. Sustainable air travel using renewable fuels like SAF is essential for reducing GHG emissions in aviation and addressing climate change.
SAF is currently pricier than regular jet fuel because of limited production. But, working together, governments, industry, and regulators can make SAF more affordable. As more SAF production pathways are developed, the aviation sector can meet its ambitious goals, reducing emissions and ensuring a green future for flying.


SAF production pathways and blending limitations
The aviation world is exploring different ways to produce sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). There are seven methods for making SAF that are approved by ASTM. These methods utilise various materials and processes to convert them into fuel.
These methods include Fischer-Tropsch Synthetic Paraffinic Kerosene, Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty Acids, among others. Each one employs different materials and approaches to produce the fuel.
Understanding Approved SAF Pathways and Fuel Standards
Each SAF production process has its own fuel blending limitations, which can range from 10% to 50% depending on the method used. This is necessary to ensure compatibility with older aircraft engines and fuel systems.
ASTM standards, such as ASTM D7566 and ASTM D1655, establish the rules for fuel quality. They ensure that SAF-based fuels are safe and perform effectively in aircraft. These regulations are stringent to maintain safety for all.
Newer engines may allow for greater SAF usage in the future, with the potential for 100% SAF by 2030. The industry is actively testing SAF to ensure it is safe and performs well.
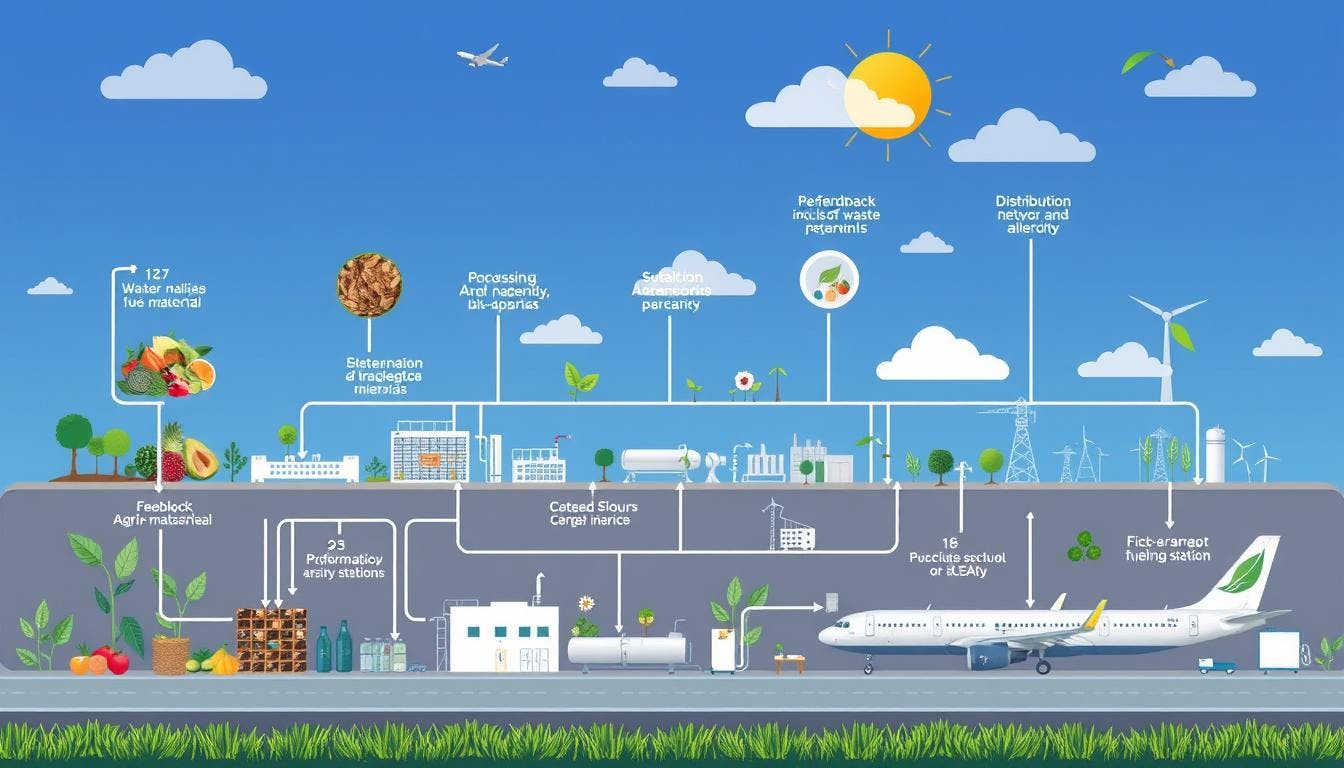
Distribution and supply chain of SAF
Adding sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) to the aviation fuel chain presents both a challenge and an opportunity. SAF must be blended with Jet A fuel before it can be used in aircraft. This requires effective collaboration between the emerging SAF industry and the existing fuel supply network.
SAF can be mixed with Jet A at oil refineries, facilitating its transportation through pipelines to airports. Alternatively, it can be blended at biofuels plants and then delivered to airports by truck or pipeline.
The supply chain is adaptable, allowing SAF and Jet A to be combined at various points. This means airports do not need to alter their fuel handling processes and can continue using the same pipelines and trucks.
Creating a robust SAF supply chain is essential for increasing its adoption. This involves collaborating with local groups, employing data tools, supporting initiatives, and investing in large-scale SAF production facilities.
By leveraging existing resources, such as corn ethanol and oil refinery infrastructure, the aviation sector aims to accelerate SAF production. This will help achieve its significant sustainability goals.

Research and development initiatives for SAF
We are dedicated to enhancing sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). This will help the aviation sector become more environmentally sustainable. We collaborate with governments and other stakeholders to improve SAF production and utilisation.
We examine how to make SAF more affordable and accessible. This includes assessing whether we have the appropriate infrastructure and supply chain. Our goal is to make SAF a common choice for air travel.
Government agencies' efforts in SAF R&D
The U.S. Department of Energy, the U.S. Department of Transportation, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture lead efforts in SAF research. They have ambitious plans to increase SAF usage, aiming for 3 billion gallons by 2030 and 35 billion gallons by 2050.
They also seek to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 50%. They are exploring new methods to produce SAF, including utilising wet waste, bio-based polycyclic alkanes, and carbon-rich waste gases.
These efforts help us realise SAF's full potential. We are working to make air travel more sustainable. By innovating together, we are making a more responsible future for aviation a reality.
17 South Street
Auckland 1010
New Zealand
info@carbonclick.com- -
- X
Subscribe now to stay up to date with CarbonClick, carbon offsetting and climate action.
By signing up you agree to our Privacy Policy.


